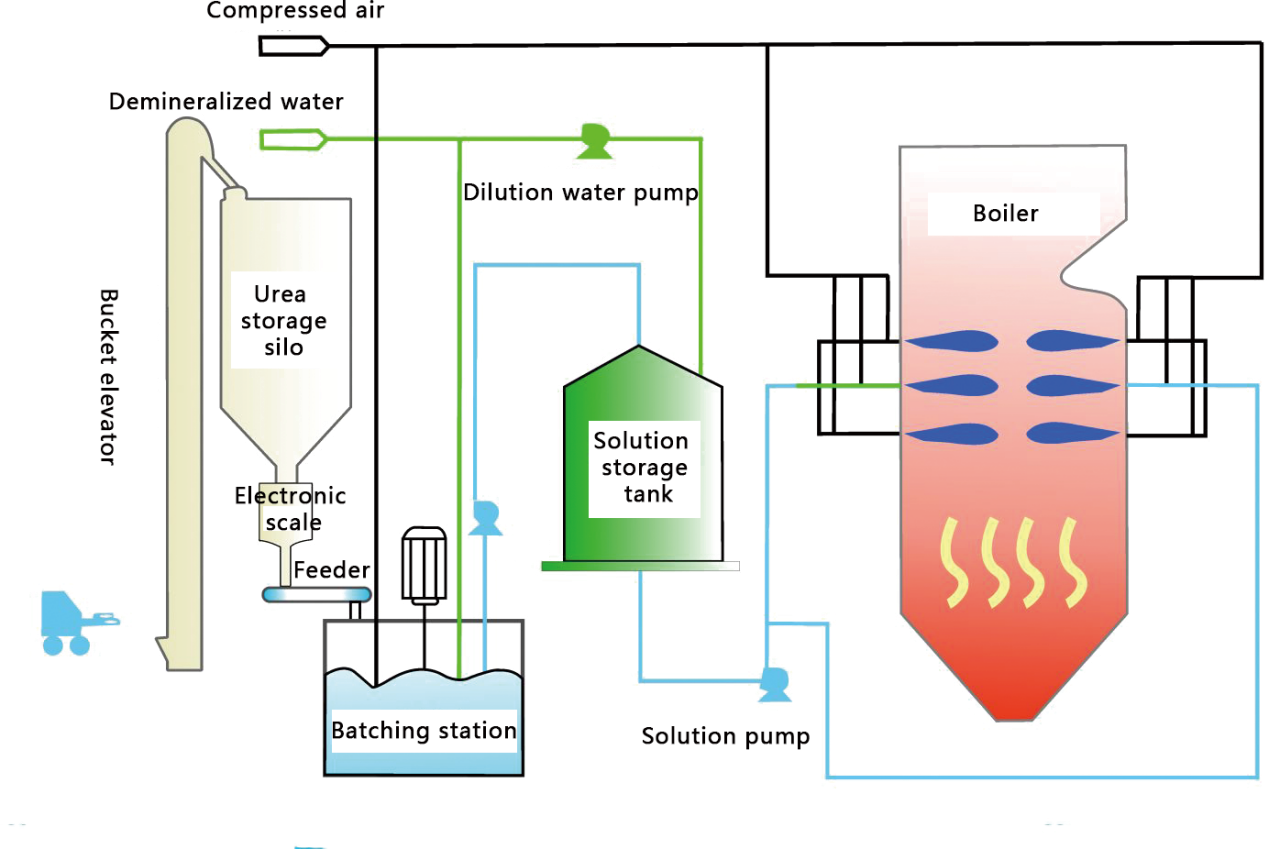
Selective Non Catalytic Reduction (SNCR): Principle: Without using a catalyst, ammonia or urea or other reducing agents are injected into the furnace temperature range of 850-1100 ℃ to reduce nitrogen oxides to nitrogen gas. Advantages: Relatively low investment cost and short construction period.
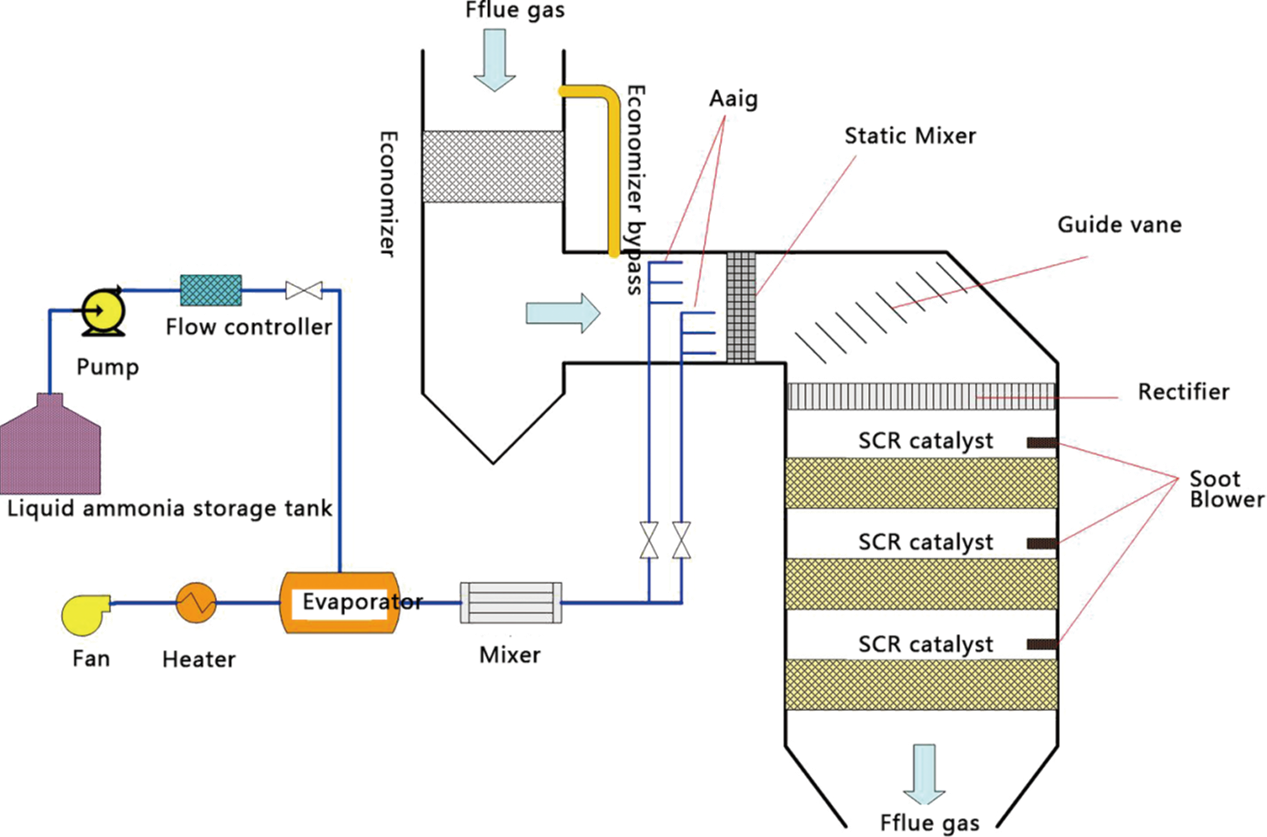
1.High NOx removal efficiency The removal rate of SCR method can be maintained between 70% and 95%, and the NOx outlet concentration can be reduced to around 50mg/m3, making it an efficient flue gas denitrification technology. 2.Low secondary pollution The basic principle is to use a reducing agent to reduce NOx to non-toxic and harmless N2 and H2O,and the ammonia leakage is low (0-8mg/Nm3). 3.The technology is relatively mature and widely used It has been widely used both domestically and internationally, and is widely used in gas, ail, and coal-fired boilers.